What Does A Prostate Exam Look Like?
Examining the prostate is vitally important for men at certain ages. Thus, prostate cancer can be detected early and treated in a timely manner.
Examination of the prostate is a subject that is often taboo among men. For many, it means an invasion of privacy that they are not prepared to experience. However, it has become more and more accepted over time.
The prostate is a gland that only men have. It is located under the bladder and wraps around the urethra. Its function is to produce fluids which will later form semen.
Over the years, the prostate gradually increases in size. It is a phenomenon that all men submit to because of their age. We know that by the age of eighty, almost 70% of them have abnormal gland growth.
Prostate cancer is the most aggressive and deadly form of this enlarged gland. It is one of the most common cancers in men and is responsible for significant mortality.
Just as the Pap smear and mammogram are tools for preventing cancer disease in women, so are they in men. The prostate exam is the prevention tool for men.
An examination of the prostate initially involves two practices: measurement of prostate antigen and a digital rectal examination. If either or both produce altered results, the second diagnostic phase is passed with imaging and biopsy of the prostate.
But let’s see first, before we detail each prostate exam, who should undergo them.
Indications for prostate examination
It is important to clarify that the prostate exam is not for every man. Medical science has established ages and protocols for determining who benefits from screening and who does not.
The main parameters are related to the patient’s age:
- Over 50 : These men are indicated for a prostate exam every year or every two years
- Between 45 and 50 years : this age group should be screened if they have risk factors for prostate cancer. For example, people of black descent or those whose family member has been diagnosed with prostate cancer
- Under 40 : It is rare for a person under 40 to have an indication for prostate screening. Men with more than one close relative with prostate cancer are considered candidates
When the need for a prostate exam becomes clear, the doctor will order a measurement of prostate antigen and a rectal exam. The measurement is performed with laboratory techniques using a blood sample and a digital rectal exam in the same office.
If the lab results are normal, the patient will need to retest a year later. In some cases, in the absence of risk factors, measurement of prostate specific antigen can be scheduled every two years.

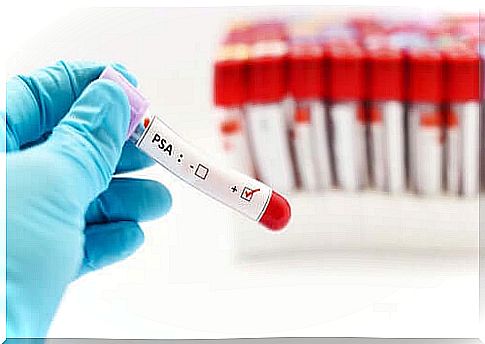
Prostate specific antigen or PSA
The PSA test is a building block of the prostate exam. This involves measuring a substance produced by the prostate in the blood. In the case of cancer, the antigen is high and its detection alerts us to the pathological process.
However, there may also be an elevation in PSA levels for other non-oncological reasons. There is a high APS when:
- The patient underwent a transrectal ultrasound
- Prostatitis : infections in the prostate increase the level of PSA
- Enlarged prostate : The hypertrophy called benign prostatic hyperplasia also changes the value, but less pronounced than cancer
Normal baseline PSA values in humans are less than 4 ng / mL. Between 4 and 10 ng / mL, there is a possibility of prostate cancer. With a PSA greater than 10, the risk of cancer is very high.
Rectal examination
The digital rectal exam is the other part of the prostate exam. The test involves inserting an examiner’s finger through the patient’s rectum to palpate the gland.
The procedure is done with gloves and lubrication to reduce discomfort. The patient is suggested to assume a lateral position lying on the table and, if possible, a fetal position, as these are the least uncomfortable and painful modalities.
The examiner, doctor or nurse, seeks to directly palpate the prostate near the rectum. Therefore, it can be achieved with this maneuver. Palpation is aimed at detecting any lump or hardening indicating an abnormal process.
If an abnormality is detected, it will suggest the need for further studies. Even more if accompanied by a high PSA result.
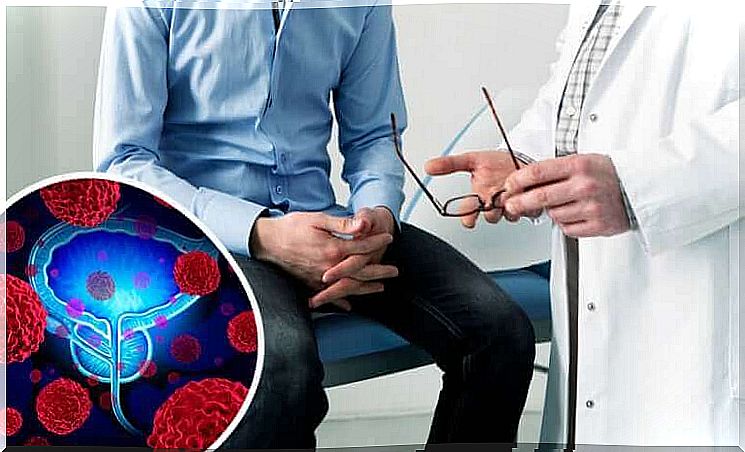
What to do if you have an abnormal prostate exam
The next step in an abnormal prostate exam is to request imaging tests to clarify the diagnosis. Your doctor may order ultrasounds and, if necessary, a biopsy of the gland.
Early detection is essential. Taken early, this tumor is completely treatable and manageable. Health teams insist on prostate screening because it is very effective in reducing the number of deaths from this cancer.
It is fundamental to lose the fear of this examination as a man and to carry it out when it is indicated. The annual health check can add many years to your life.