Hyperkalaemia: Description And Treatment
When a person suffers from hyperkalaemia, their level of potassium in the blood is above normal. There are different treatments to restore balance.

Hyperkalaemia is an alteration in the level of potassium concentration in the blood. In this case, there is an excess of potassium. When, on the contrary, there is a lack of potassium, we speak of hypokalemia.
It is necessary to have in mind that hyperkalemia is recognized when the concentration ratio of the electrolyte is greater than 5.5 mmol / L.
What is Potassium What’s the point ?
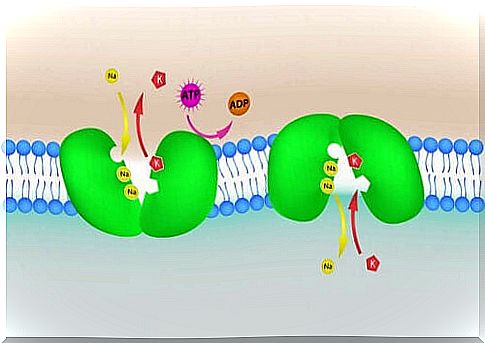
Potassium is a chemical element whose symbol in the periodic table is “K”. It is a soft alkali metal which has important functions, both at the muscular level and at the level of the nervous system.
Moreover, this alkali metal is also an electrolyte, just like calcium and closes it. These electrolytes help balance the pressure and concentration of substances inside and outside cells.
Here are the most important roles played by this element in the body:
- Skeletal development
- Osmotic balance
- Protein synthesis
- Nerve transmission
- Muscle contraction
Cause of hyperkalemia
Usually, this is caused by a decrease in the renal excretion of potassium. Abnormal movement of potassium out of cells is also often the cause of this disorder.
Several factors contribute to the development of hyperkalaemia. We can, among others, list the following:
- Increased potassium intake
- Administration of certain drugs which affect the renal excretion of potassium
- Acute kidney injury
- Chronic nephropathy
Another cause of this alteration may be the presence of metabolic acidosis, such as that found in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis.
On the other hand, pseudo-hyperkalemia, the artificial increase in potassium, can also degenerate into hyperkalemia. It can be caused by prolonged application of a tourniquet or by excessively tightening your fist during a blood test.
Likewise, thrombocytosis is sometimes the cause of pseudo-hyperkalaemia. This is because the potassium in platelets is released during clotting.
Symptoms
In most cases, hyperkalemia goes unnoticed. This implies that the variation in potassium levels is not detected by any symptoms and, therefore, only a biological examination can detect it.
In cases where there are symptoms, they depend on the severity of hyperkalemia and how quickly it appears. As a rule, the first symptoms are as follows:
- Muscular weakness
- Tremors in the arms or feet
- Tingling
- Paresthesia of the fingers or feet
In addition, these symptoms are usually accompanied by insomnia, nausea, vomiting, and decreased heart activity.
In the most severe cases, the patient may suffer from cardiac arrhythmias. This is due to the fact that the heart is an organ that needs potassium in order to contract and for the proper conduct of its functions. When we talk about arrhythmia, we mean that disorder in which the heartbeat affects the frequency, intensity and regularity of nerve impulses.
How to diagnose hyperkalemia?

This condition can be identified by measuring the serum electrolyte concentration against the control level. This check is done when an EKG is performed on a patient and the variations in this concentration are observed.
Patients with altered EKG results are usually those with renal failure, advanced heart failure, urinary obstruction, and those treated with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors). ). Ultimately, to achieve a correct diagnosis, the following tests must be carried out:
- Measurement of serum potassium
- ECG
- Review of the list of drugs consumed
- Kidney function assessment
What treatment?
The goal of any treatment will be to reduce the level of potassium in the blood. In addition, these will also aim to eradicate the origin of this disorder, such as, for example, stopping the intake of hyperkalaemic drugs.
In situations where the increase in potassium levels is moderate, treatment is put in place to reduce it, for example, certain drugs such as potassium exchange resins are administered. It is also possible to prescribe diuretics or perform dialysis.
In hyperkalaemia measured at a level above 6.5 mmol / L without alteration of the electrocardiogram, salbutamol or baking soda are two very effective drugs.
Finally, when the potassium level above 6.5 mmol / L is accompanied by an alteration in the ECG, the first thing to do is to protect the heart. For this, we administer, in general, calcium in order to reduce serum potassium (potassium level in the blood).
All the information shared in this article does not preclude immediate medical attention if you notice any symptoms of this disease. Only the specialist can recommend the best treatment for you.