Causes And Symptoms Of Sight Loss
Sudden loss of sight is a major problem that should never be ignored. We’ll walk you through some of the most common causes and symptoms.

Sight is, without a doubt, one of the senses that we use the most. It is for this reason that the loss of sight is a serious problem, which changes our life in a radical way. Do you want to know what are the causes and symptoms of this problem? We explain all of this to you below.
First of all, for there to be a decrease in visual acuity, one of the organs involved in sight must be affected. In other words, partial or total blindness occurs when there is a problem with the cornea, lens, retina or optic nerve.
Causes of partial blindness
When we refer to partial blindness, we are talking about some people who, although their visual acuity is reduced, are still able to distinguish certain shapes, lights and shadows. At this time, there is no complete loss of the sense of sight, but it is more complicated to use it.
Depending on its origin, this type of blindness can be chronic or acute. We will look at the most common causes of partial sight loss.
Corneal damage
Any lesion on the surface of a tissue generates a scar, and the cornea is no exception. This scar removes the transparency of the cornea, which prevents light from reaching the retina and causes a decrease in visual acuity.
Corneal damage can have different origins, from severe infections to direct trauma. Any stimulus that can damage its cells to a certain depth can cause partial blindness.
The affected visual field is then changed depending on the location and size of the scar. In this sense, there is no list of defined and general symptoms. Nevertheless, some of the following symptoms can be seen:
- Blurred vision: part of the field of vision is black or opaque.
- Pain : accompanied by itching in the affected eye.
- Sinking eyes.
- Red spots.
- Sensation of sand in the eye : as if there was something encrusted under the eyelid.
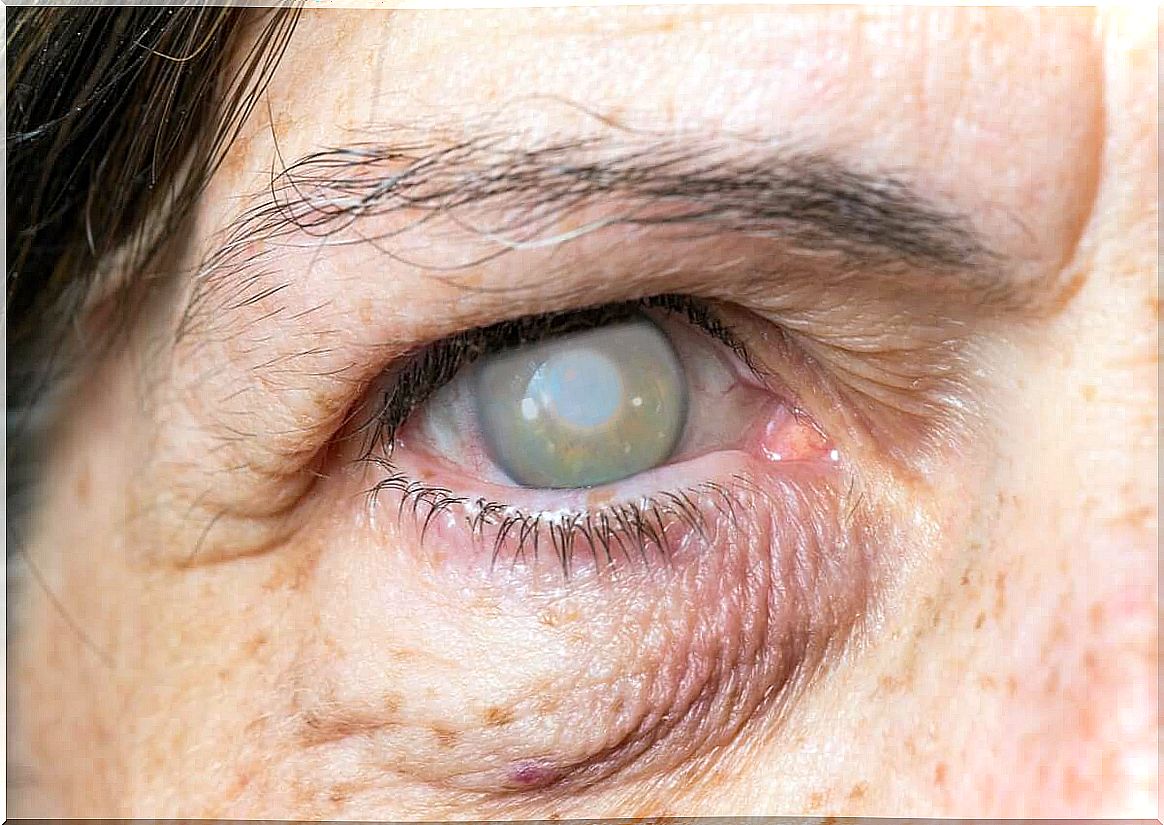
Cataracts
The other most common causes of partial blindness are cataracts. These are areas of opacity in the lens, which is the eye’s primary means of refraction. This opacity prevents light from properly reaching the retina, resulting in partial loss of sight.
In most cases, cataracts appear when the lens degenerates or is damaged. According to several studies, cataracts are the cause of 47.9% of partial blindness in the elderly.
Some of the main symptoms that people with cataracts suffer from include blurry, cloudy, or blurred vision, washed out colors, and an inability to see properly at night. They also say they see the light sources in a very bright way, with a sort of halo around, as if they were seeing double.
Retina problems
The retina is the part of the eye that is responsible for translating the light signals sent by the lens for the brain to analyze. This implies that any injury there can lead to loss of sight.
In most cases, retinal problems are created by faulty capillaries. These then let fluid escape into the tissues. Thus, among the most common causes we can find the following:
- Diabetic retinopathy.
- Obstruction of the arteries or veins in the eye.
- Tearing of the retina.
- Partial retinal detachment.
- Hypertensive retinopathy.
On the other hand, there are other types of retinal damage that are not related to the presence of fluids. Macular degeneration is one example. In this situation, the center of the retina begins to deteriorate, which generates blurred vision and a blind spot in the visual field.
Finally, various ailments caused by fungi, parasites or bacteria can seriously damage the retina. This is the case with ocular toxoplasmosis, which is very common in immunocompromised people.
Optic nerve problems
The optic nerve is responsible for transmitting all the information captured by the retina to the brain. Therefore, its role is also essential in the vision. Problems related to this structure generally affect one or more visual fields.
In most cases, these problems are the result of glaucoma. The latter is a common disease that causes an increase in intraocular pressure and affects the nerve. It is therefore unable to transmit signals correctly, making vision difficult.
However, there is another set of conditions that can lead to partial blindness by affecting the optic nerve. This is the case with optic neuritis, or inflammation of the nerve. In addition, strokes or tumors can also have an indirect effect on the central nervous system.
It is important to clarify that the symptoms of optic nerve damage can vary depending on their etiology. However, those affected often suffer from rapid vision loss, a reddish patch in one or more visual fields, double vision, and eye pain.
Causes of total blindness
On the other hand, there is total blindness. The affected person is then unable to distinguish either light or shadow. The situations that can cause total vision loss can be the same as those that cause partial blindness, except that the symptoms are then in their terminal stages.
Trauma or serious injury
When the trauma is very severe and affects the entire cornea, it can lead to total blindness. One of the most common causes of this type of injury are chemical burns.
However, corneal damage is not the only one affecting visual acuity. Trauma to the head or eyeball, whether with a sharp or blunt object, can damage the optic nerve and the retina.
Complete retinal detachment
We have mentioned partial detachment as a cause of partial blindness. However, if not treated in time, the detachment can progress and end up being complete, completely preventing vision.
In the majority of cases, this happens due to the presence of fluid in the posterior part of the retina. This will isolate the tissues of the eyeball, which will interrupt the blood supply and cause ischemia and death to the area.
Although it may be asymptomatic and painless at first, some people experience the following symptoms:
- Appearance of spots in the field of vision.
- Flashes of light in all visual fields.
- Blurry vision.
- Sudden loss of peripheral vision and later central vision.
End-stage diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is one of the complications of diabetes mellitus or diabetes mellitus. This affects the capillaries of the retina, which then allow liquid to pass to the retina and allow the deposition of substances. In addition, some healthy blood vessels can eventually become blocked.
The early stages of the disease can lead to partial blindness. However, if allowed to progress, it can lead to complete loss of vision. This is because at the final stage new, very thin-walled blood vessels form in an attempt to irrigate the tissues properly. These new capillaries are liable to rupture at any time and generate retinal hemorrhage.
Endophthalmitis
An uncommon cause of vision loss is endophthalmitis. This is an infection of the inside of the eye that should always be considered a medical emergency.
This infection is triggered, in large part, by the entry of external microorganisms, after surgery or eye injury. However, it can also be caused by an internal septic infection that has affected the eye.
Among the symptoms described by people with endophthalmitis, we can distinguish severe pain with red eyes and the appearance of a yellow, white or purulent secretion inside the eyeball. The eyelids are also inflamed.
Vascular occlusion
All the blood vessels in the body are susceptible to clogging. An occlusion of those of the retina or optic nerve can induce painless loss of sight.
If the affected blood vessel is the central retinal artery or the optic nerve artery, there is an inadequate blood supply to the tissues. This then leads to a lack of oxygen, and these can swell and be permanently damaged.
On the other hand, if it is the central vein of the retina that is affected, the blood drainage will be inadequate. This then leads to engorgement, that is to say an excessive accumulation of fluid in the tissues which will lead to blindness.
When to see a doctor in case of sight loss?
Loss of sight, whether total or partial, should always be considered a medical emergency. In many cases, it is not accompanied by pain, but that does not mean that it is less severe. It should never be ignored.
For this reason, it is imperative to consult a specialist as soon as possible so that he can perform the necessary examinations and provide a reliable diagnosis. In many cases, there is only a short time to act before the damage is irreversible.
It is important to clarify that irreversible loss of vision involves an inevitable change in lifestyle. Fortunately, there are many alternatives nowadays for people with visual impairments to be able to carry out their daily activities without inconvenience.